Ethylene oxide production is essential in the chemical industry, providing the foundation for creating numerous critical products. It supports industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and agriculture. For businesses seeking to understand this versatile compound better, this guide explains production methods, applications, and the importance of safety and sustainability.
What is Ethylene Oxide?
Ethylene oxide (EtO) is a highly reactive, flammable gas widely used for its versatility in various applications. Furthermore, its ability to undergo polymerization and chemical reactions makes it a cornerstone for producing essential industrial and consumer products.
Key Properties of Ethylene Oxide:
- Chemical Formula: C2H4O
- Physical State: Gas at room temperature, easily liquefied under pressure
- Applications: Critical in healthcare, agriculture, and industrial manufacturing
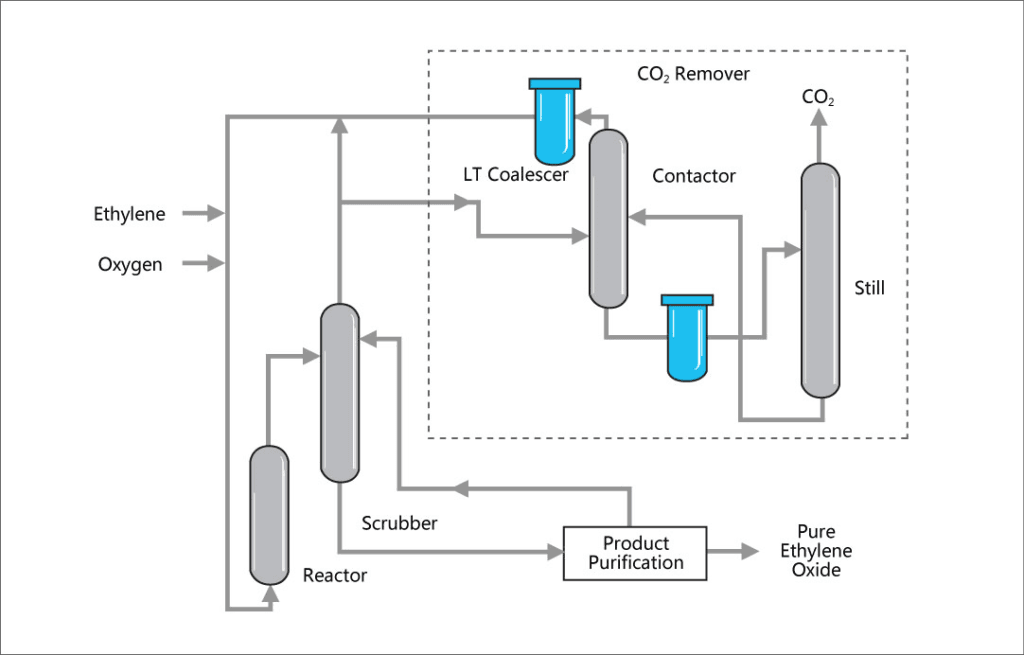
How is Ethylene Oxide Produced?
Producing ethylene oxide involves highly controlled methods to ensure efficiency and safety. The process primarily relies on the oxidation of ethylene, a widely available hydrocarbon.
1. Direct Oxidation Process
The direct oxidation process is the most popular and efficient method of ethylene oxide production. It combines ethylene with oxygen in the presence of a silver catalyst, ensuring high yield and minimal by-products.
Reaction:
C2H4+12O2→C2H4OC2H4+21O2→C2H4O
- Catalyst: Silver-based catalysts improve reaction speed and reduce energy consumption.
- Conditions: The reaction takes place at 200-300°C and moderate pressure.
- Advantages: This method minimizes waste and enhances productivity.
2. Chlorohydrin Process
Although less common today, the chlorohydrin process was historically used for ethylene oxide production. It involves reacting ethylene with hypochlorous acid to form ethylene chlorohydrin, followed by treatment with lime to produce ethylene oxide.
Reaction:
C2H4ClOH+Ca(OH)2→C2H4O+CaCl2+H2OC2H4ClOH+Ca(OH)2→C2H4O+CaCl2+H2O
- Disadvantages: Higher environmental impact and lower efficiency compared to the direct oxidation process.
Applications of Ethylene Oxide
Ethylene oxide has broad applications across various sectors, making it indispensable for modern industries.
1. Medical Sterilization
To ensure the sterility of medical tools and supplies, ethylene oxide is commonly used in healthcare. Its ability to penetrate packaging and eliminate microorganisms ensures a high level of safety.
2. Chemical Synthesis
Ethylene oxide is also vital for producing ethylene glycol, a key ingredient in antifreeze, polyester fibers, and resins. Its role in chemical synthesis underpins many everyday products.
3. Consumer Goods
Moreover, ethylene oxide is used in manufacturing detergents, surfactants, and cosmetics, contributing to improved product functionality and performance.
4. Agriculture
In agriculture, ethylene oxide serves as a fumigant to control pests and sterilize food products, ensuring long-term storage safety.
Why is Ethylene Oxide Production Important?
The importance of ethylene oxide lies in its ability to support diverse industries. This compound’s versatility ensures its applications continue to grow alongside industrial advancements.
Benefits of Ethylene Oxide Production:
- High Reactivity: Enables efficient chemical reactions and product synthesis.
- Versatility: Suitable for applications in healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing.
- Economic Impact: Drives innovation and supports global supply chains.
Ensuring Safety and Sustainability in Ethylene Oxide Production
Since ethylene oxide is flammable and toxic, strict safety and environmental measures are necessary during production and handling.
1. Safety Protocols
To minimize risks, facilities incorporate advanced monitoring systems to detect leaks, maintain proper ventilation, and train workers extensively.
2. Sustainability Initiatives
Producers are also adopting eco-friendly practices, such as using energy-efficient catalysts and controlling emissions, to reduce environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the most efficient method for ethylene oxide production?
The direct oxidation process is the most efficient and widely used method, offering high yield and reduced waste.
2. What industries benefit from ethylene oxide?
Industries such as healthcare, chemicals, agriculture, and consumer goods benefit significantly from ethylene oxide’s versatility.
3. How can the environmental impact of ethylene oxide production be reduced?
Using advanced catalysts, automated systems, and emission controls can help lower the production process’s environmental footprint.
Conclusion
Understanding ethylene oxide production is vital for businesses that rely on this compound’s unique properties. By adopting efficient processes and sustainable practices, manufacturers can meet global demand while minimizing environmental impact.
For more insights on ethylene oxide production and its industrial applications, explore our resources today.



